Events
| Event name | Event key |
|---|---|
| Snapshot status changed | member_snapshot.status_change |
| Snapshot Fulfillment Summary updated | member_snapshot_carrier_fulfillment_status.status_change |
| Difference created | difference.created |
| Difference marked as a discrepancy | difference.discrepancy |
| Difference resolved | difference.resolved |
| Difference replaced | difference.replaced |
| Group Created | group.created |
| Group Connection Request created | group_connection_request.created |
| Group Connection Request status changed | group_connection_request.status_change |
| Group Disconnection Request created | group_disconnection_request.created |
| Group Disconnection Request status changed | group_disconnection_request.status_change |
Payload Structure
The webhook HTTP payload will include information in both its HTTP headers and its request body. Event payloads do not contain any PII or PHI. Noyo recommends using the corresponding Get difference when you receive any.created webhook.
Headers
The payload will be sent with the following HTTP headers:Common fields
Each webhook event contains the following fields in the response body:Using webhooks to track enrollment changes
Our The Tracking API and its webhooks enable you to build field-level change tracking, so you have complete transparency from the time Noyo initially processes the member snapshot to when we confirm the change was made successfully by the carrier. You can also listen for unexpected data discrepancies that could interrupt coverage for your members.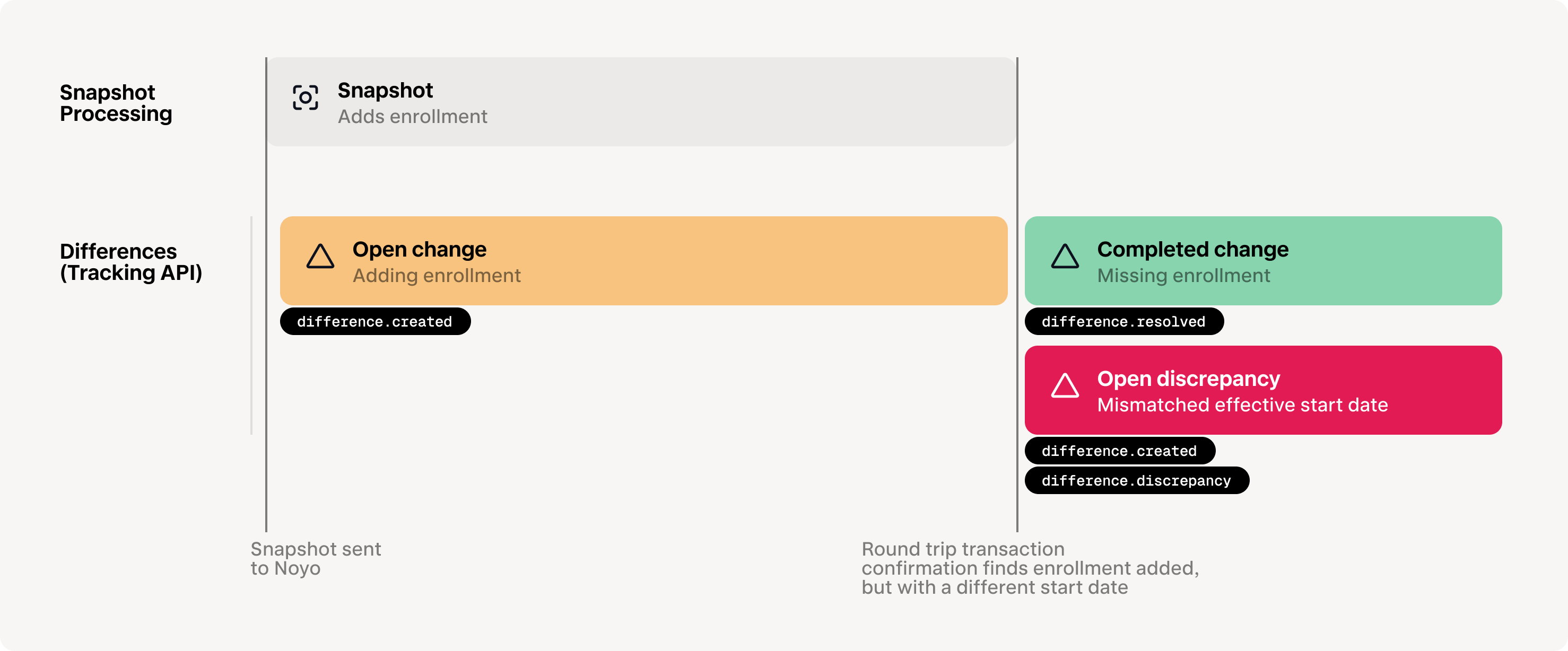
Member Snapshot status changed
JSON
Member Snapshot Fulfillment Summary updated
Read more about fulfillment summary here.Difference created
For any snapshot sent to Noyo that contains changes, adifference.created event will be sent almost instantly after the snapshot is initially processed. This means you can save individual tracking identifiers for all field-level changes that are in-process.
Note that discrepancies found during carrier syncs will also initiate a difference.created event, so Noyo suggests calling Get difference to populate all relevant details of the difference, such as its source.
Difference marked discrepancy
If we detect that a processing change has not been made by the carrier, or we find a data discrepancy during a sync, Noyo will send adifference.discrepancy event.
Difference replaced
In cases where an open difference is replaced by another, Noyo will send an event that you can use to replace the association in your system.Difference resolved
When a change is completed successfully by the carrier or a discrepancy is resolved (whether due to a subsequent snapshot, a sync, or a manual portal update, Noyo will send adifference.resolved event.
Group Connection Request created
Group Connection Request status changed
Group Disconnection Request created
Group Disconnection Request status changed
Subscriptions
Create a subscription
You can create webhook subscriptions in Command Center by going to Developer > Webhooks and pressing “New subscription”.- Under “Destination”, type the URL where you’d like to receive webhooks
- Under “Secret”, type a string to use as a
secretkey. You should choose a random string of text with high entropy. You can use the webhook secret to limit incoming requests to only those originating from Noyo. You may optionally provide an API key name to assist in future key rotation
Testing
Send a test event for a subscription
You can send a test request to any subscription through Command Center. The payload will resemble the following:Best Practices
Event delivery and ordering
New event types will be continuously added; it is up to you to decide which events you want to process and how, but your implementation of the event listener must be able to handle new event types without breaking. We guarantee at-least-once delivery of events, meaning webhook endpoints may occasionally receive duplicate events. All event requests include an event ID, which may be used to deduplicate webhook events. We do not guarantee delivery of events in the order they happen. You should also use the Noyo REST APIs to fetch any missing data.Verification
Authenticate all requests to your webhook endpoint. Noyo includes an HMAC signature with each outgoing webhook request in anx-noyo-signature HTTP header. Endpoints should verify each request by: computing an expected HMAC signature for the payload and verifying that the value contained in the x-noyo-signature header provided by the sender matches the expected signature. Read more.
Responding to webhooks
In order to prevent unnecessary retries, we recommend receiving webhook events and processing them in separate processes. Upon receiving the event, you should immediately respond with a200 indicating that the event was successfully delivered.
Subscription health and retries
- When an event fails to deliver, its queue will handle retrying with backoff 15 times over 3 days.
- When a webhook fails delivery, its subscription is moved into
unhealthystatus- If an event succeeds, the status is changed back to
active - If an event comes in when a subscription has been unhealthy for 7 days, and that event fails, the subscription is changed to “failed.” The subscription’s queue is paused, which means that no other events will be attempted
- If an event succeeds, the status is changed back to
